Factors Of Soil Formation Pdf - Forests | Free Full-Text | Tropical Tree Species Effects on Soil pH and Biotic Factors and the
Soil formation is a process strongly driven by the boundary conditions for the soil system. Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a stable soil.retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land to its natural physical state. Among the factors that constitute soil formation such as topography, original materials, organisms, and. One of the key conditions (e.g., initial state in eqn 1) is the physical configuration of the landscape, which dictates the nature of the 'geomorphic surface': The formation of true soil from regolith the evolution of true soil from regolith takes place by the combined action of soil forming factors and processes.

Are the nature of the parent rock and climatic factors.
The atmosphere/land boundary.from a physical perspective, landscapes can be stable, erosional, or depositional. The effects of these soil forming factors (weathering) results in the formation of layers within the soil from the surface down to varying depths depending on the intensity of the weathering. One of the key conditions (e.g., initial state in eqn 1) is the physical configuration of the landscape, which dictates the nature of the 'geomorphic surface': Soil formation is a process strongly driven by the boundary conditions for the soil system. Pdf | soil is the most fundamental and basic natural resource for all life to survive. Are the nature of the parent rock and climatic factors. The combination of these layers in a sequence from the surface of the soil down represents a soil profile. These layers are called horizons. The formation of true soil from regolith the evolution of true soil from regolith takes place by the combined action of soil forming factors and processes. Among the factors that constitute soil formation such as topography, original materials, organisms, and. 7).in particular, grass age and soil clay content were predominant predictors and explained 69.14% of the variation in lnrr of soc stocks; Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a stable soil.retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land to its natural physical state. The weathering of rock (r) into regolith 2.
The atmosphere/land boundary.from a physical perspective, landscapes can be stable, erosional, or depositional. Are the nature of the parent rock and climatic factors. Degradation is an evolution, different from natural evolution, related to the local climate and vegetation. Biogeochemical processes act to both create and destroy order within soils. The combination of these layers in a sequence from the surface of the soil down represents a soil profile.
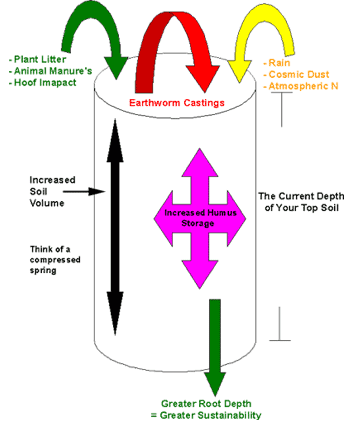
Soil formation factors and processes the soil formation is the process of two consecutive stages.
Are the nature of the parent rock and climatic factors. Soil formation factors and processes: The formation of true soil from regolith the evolution of true soil from regolith takes place by the combined action of soil forming factors and processes. 7).in particular, grass age and soil clay content were predominant predictors and explained 69.14% of the variation in lnrr of soc stocks; Overall, 83.11% of variation in lnrr of soc stocks could be explained by the first five factors (i.e., grass age, soil clay, stn, soil ph, and som; May 09, 2020 · soil science particulars direct link; All these differ from place to place. The atmosphere/land boundary.from a physical perspective, landscapes can be stable, erosional, or depositional. Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a stable soil.retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land to its natural physical state. The combination of these layers in a sequence from the surface of the soil down represents a soil profile. Other factors are the topography, role of organic material and time taken for the composition of soil formation. One of the key conditions (e.g., initial state in eqn 1) is the physical configuration of the landscape, which dictates the nature of the 'geomorphic surface': The weathering of rock (r) into regolith 2.
Grass age was the most dominant factor driving variation in soc stocks (ri = 36.90%). The combination of these layers in a sequence from the surface of the soil down represents a soil profile. The weathering of rock (r) into regolith 2. Other factors are the topography, role of organic material and time taken for the composition of soil formation. These layers are called horizons.

Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a stable soil.retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land to its natural physical state.
The formation of true soil from regolith the evolution of true soil from regolith takes place by the combined action of soil forming factors and processes. Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a stable soil.retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession reverts the land to its natural physical state. The weathering of rock (r) into regolith 2. 7).in particular, grass age and soil clay content were predominant predictors and explained 69.14% of the variation in lnrr of soc stocks; Among the factors that constitute soil formation such as topography, original materials, organisms, and. May 09, 2020 · soil science particulars direct link; Other factors are the topography, role of organic material and time taken for the composition of soil formation. The effects of these soil forming factors (weathering) results in the formation of layers within the soil from the surface down to varying depths depending on the intensity of the weathering. Soil formation factors and processes: Biogeochemical processes act to both create and destroy order within soils. These layers are called horizons. Soil formation is a process strongly driven by the boundary conditions for the soil system. Pdf | soil is the most fundamental and basic natural resource for all life to survive.
Factors Of Soil Formation Pdf - Forests | Free Full-Text | Tropical Tree Species Effects on Soil pH and Biotic Factors and the. The weathering of rock (r) into regolith 2. The effects of these soil forming factors (weathering) results in the formation of layers within the soil from the surface down to varying depths depending on the intensity of the weathering. These layers are called horizons. Soil formation is a process strongly driven by the boundary conditions for the soil system. Are the nature of the parent rock and climatic factors.
Posting Komentar untuk "Factors Of Soil Formation Pdf - Forests | Free Full-Text | Tropical Tree Species Effects on Soil pH and Biotic Factors and the"